Sign up to save your library
With an OverDrive account, you can save your favorite libraries for at-a-glance information about availability. Find out more about OverDrive accounts.
Find this title in Libby, the library reading app by OverDrive.



Search for a digital library with this title
Title found at these libraries:
| Library Name | Distance |
|---|---|
| Loading... |
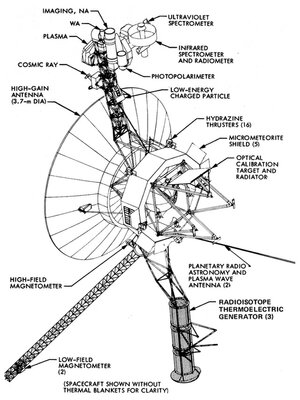
The Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 spacecraft are twin robotic space probes launched by NASA in 1977. Their primary mission was to study the outer planets of our solar system, and they have since become humanity's farthest-reaching explorers.
Key Details:
Launch and Mission Goals
Voyager 1:
Launched: September 5, 1977
Initial Mission: To study Jupiter and Saturn, including their moons and rings.
Achievements:
Captured detailed images of Jupiter and Saturn.
Studied Saturn's moon Titan, revealing its dense atmosphere.
Now the farthest human-made object from Earth, traveling in interstellar space.
Voyager 2:
Launched: August 20, 1977 (before Voyager 1 due to a different trajectory).
Unique Achievement: The only spacecraft to visit all four outer planets—Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
Provided detailed studies of Uranus and Neptune, including their moons, magnetic fields, and ring systems.
Golden Record
Both spacecraft carry a Golden Record, a 12-inch gold-plated phonograph disc containing sounds, music, images, and greetings from Earth.
The record serves as a message to any extraterrestrial life that might encounter the spacecraft.
Current Status
Both probes have exited the heliosphere (the bubble of solar wind and magnetic fields surrounding our solar system) and entered interstellar space.
Their instruments continue to send data back to Earth, studying cosmic rays, interstellar magnetic fields, and plasma waves.
Communication: Operated via NASA's Deep Space Network (DSN).
Power: The probes use radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs), but their power is gradually diminishing.
Significance
Voyager 1 and 2 have greatly expanded our understanding of the outer planets and the interstellar environment.
They represent humanity's desire to explore and reach out into the unknown, carrying Earth's story into the cosmos







